0
- Home
- Technologies
- Services
- Products
- Glycan & Lectin Arrays
- O-Glycan Array
- N-Glycan Array
- MUC1 Glycopeptide Array 1
- MUC1 Glycopeptide Array 2New
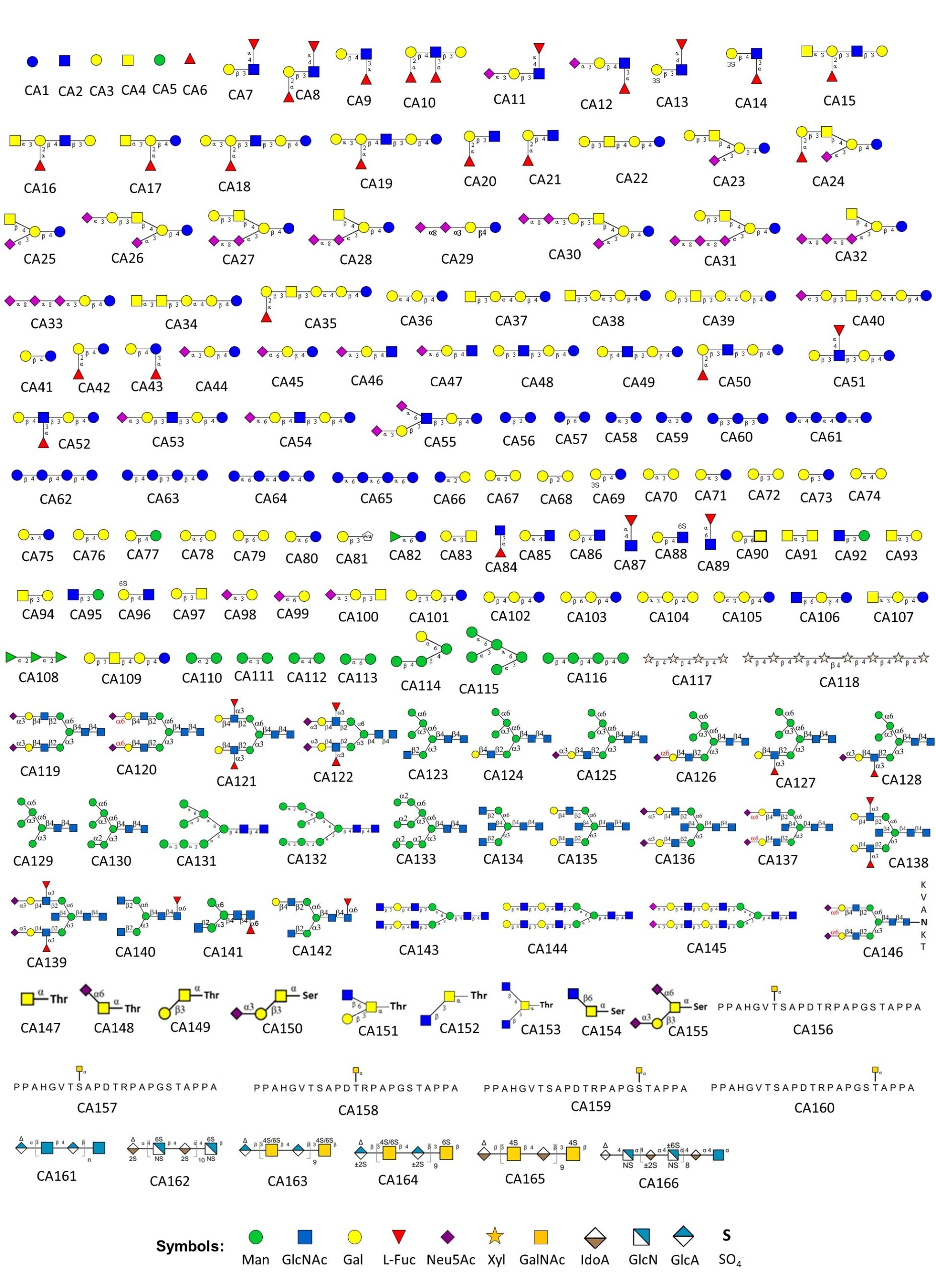
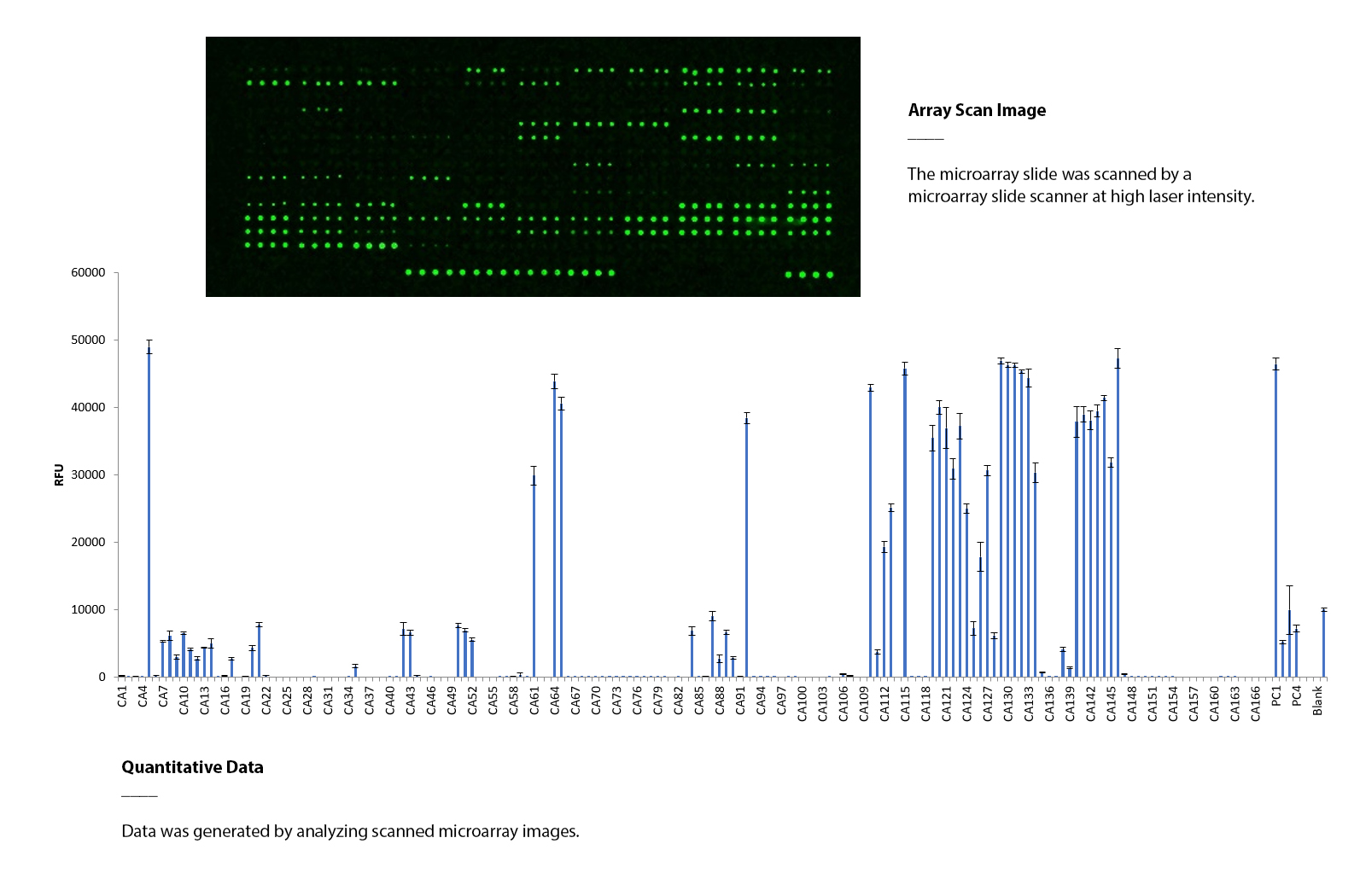
- CatchAll Glycan Array
- Poly – LacNAc Glycan Array
- Sulfated Glycan Array
- Oligomannose Glycan Array
- Glycosphingolipid Glycan Array
- Glycosaminoglycan Array
- Sialoside Array
- Heparan Sulfate Glycan Array
- Lectin Array
- Blood Group Antigen Array
- Bacterial Glycan Array
- SARS-CoV-2 RBD Peptide and Glycopeptide Array
- GlycoAntibiotic Array
- Human Milk Oligosaccharide Array
- Multivalent Microarray Slides
- Assay Buffers
- Cell Analysis
- Glycan & Lectin Arrays
- Applications
- Company
- Contact Us